Where are the funds going? Costing Basics for Farmers
20.01 2023
Planning the cost of production is an integral part of the planning of the enterprise and is a system of technical and economic calculations that reflect the amount of current costs and those that have developed throughout the entire industrial cycle. The purpose of planning is an economically justified determination of the amount of costs necessary for the production and marketing of the company's products. It is done to calculate the actual cost of production, control the use of material, labor and financial resources, as well as timely, complete and reliable determination of the actual costs associated with production.
The production cost of production is the direct costs of the main operating activity for the production of products and the allocated general production costs, expressed in cash. It is a calculated category and includes only those costs that are actually incurred by agricultural enterprises. The production cost determines the level of costs per unit of agricultural products and allows you to objectively evaluate the efficiency of production in specific business conditions.
With this in mind, the Soft.Farm team, within the framework of a subgrant from the USAID AGRO Program, expanded the capabilities of the «Production Self-Cost» function in its web service. Now, thanks to it, it is possible to calculate all the costs of an agricultural enterprise, calculate profits and, as a result, obtain a general indicator of the economic efficiency of production, as well as find the reasons for low profitability and determine reserves for reducing costs per unit of output. The calculation of the production cost in the Soft.Farm system starts automatically after the approval of technological maps. It takes place on a separate culture based on the data of the production plan and the technical map.
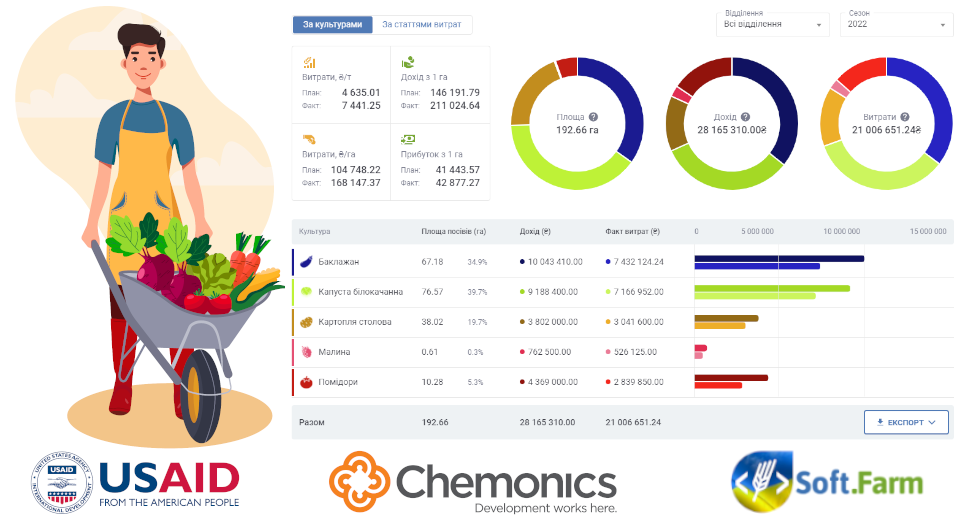
Precisely because there is always a need to analyze the results achieved in comparison with the planned ones, the new interface is structured according to planned and actual indicators. Usually, the planned cost is calculated before the start of the planning period, which allows you to organize control over the costs of funds and the economic activity of the enterprise during the season. The actual cost is calculated based on the results of economic activities based on actual costs and the volume of products received. That is, when the crops have already been collected and the actual yield is known, it is possible to carry out analysis by comparing the plan and the fact, and the Soft.Farm web service provides such an opportunity. It should be noted that only crops linked to approved technological maps, which contain a list of works and material and technical means necessary to perform these works, take part in the cost calculation. Their area makes up the structure of sown areas for each crop during the year. Income data is pulled automatically from the production plan, and the planned gross harvest specified in crops is used to calculate income.
Enterprise expenses are one of the resulting indicators of economic activity. They make up the sum of all direct costs, and their calculation is made according to the documents created in the system, such as the Tally sheet, Certificate of Completion work and Acts of writing off materials. Direct costs are displayed by crops and different items of expenditure, namely fuels and lubricants, wages, seeds, plant protection products, fertilizers and other services. Cost accounting data is used to assess and analyze the implementation of planned indicators, determine the results of the enterprise and the actual effectiveness of measures aimed at developing and improving production. At the same time, profit calculations occur by subtracting the company's expenses from its income and allow calculating profitability by comparing profits with expenses.
Cost planning helps to deeply analyze the economic condition of the enterprise and identify opportunities for increasing production efficiency, which consists in increasing crop yields through the development of precision farming tools, improving labor productivity and the overall level of mechanization.
Back to news list