Online seeding control + seeding map = impossibility of stealing seeds
07.10 2020
The autumn sowing campaign is the basis for the financial health of an agricultural enterprise for the next year. For effective management during this period, it is necessary to take into account a number of parameters that can significantly affect the final result. During sowing, the characteristics of the equipment involved, the quality of the seed used and the organization of the work process in general play an important role. But control plays a decisive role, which means having complete information about what is happening in the field.
Today, the technology of sowing seeds on modern agricultural machinery is seriously thought out and automated. There are a number of mechanical and electronic systems available to help you seed efficiently. It can be both the simplest technologies for seeding control, pre-installed at the factory, and more functional system solutions that transfer data to the software for managing an agricultural enterprise. In any case, these systems are designed to control the even distribution of seeds in each row, while observing the set seeding rate per hectare, and to signal problems.
Only a well-adjusted and tuned seeder, which does not allow noticeable deviations during operation, can efficiently cope with the seeding task. However, the likelihood of breakdowns and blockages is not excluded in the work of even the most modern agricultural machines. In addition, a significant part of the emerging problems are associated with the influence of the human factor. For example, during sowing, there was high humidity or damp seed, which constantly clogged the seed tube, and the operator simply continued to drive the plan by hectares, ignoring the warning signals of the seeding control system.
Also, no one is immune from the situation when in the middle of the field grain begins to run out in one or several banks. A very small percentage of employees will add seeds in the middle of the run and think that only one non-working section of an eight-row seeder, depending on the actual yield, can lead to losses of up to 1 ton of crop per 1 hectare of sowing!
There are often cases when, through ignorance or oversight of workers, the wrong seeding rate or fertilization is set, and the permissible speed is exceeded, which directly affects the main statistical parameters, such as the seeding density or the accuracy of the application step. In short, such situations can vary. But all such shortcomings have one thing in common — they are often revealed too late, when sifting has already been detected and losses of part of the crop are obvious, and therefore these are direct financial losses.
It is impossible to fix what is unknown, so back to the beginning: effective management is control, based on timely information about the progress of the process. Seeding control systems without online monitoring function can give a significant effect from the implementation only with a responsible attitude of personnel to its notifications. Such a system will help set up the seeding equipment, but will not protect the farm from negligence, sabotage or a bad mood of the operator.
Soft.Farm web service is the only information system on the Ukrainian market that offers the use of the online seeding control monitoring function. We are convinced that a seeding control system should protect the interests of an agricultural enterprise, preventing theft of seeds and directly affecting income even at the seeding stage. Problems in the field shouldn't be damaging. Online control, notifications to the agronomist's mobile phone — these are the tools for effective management.
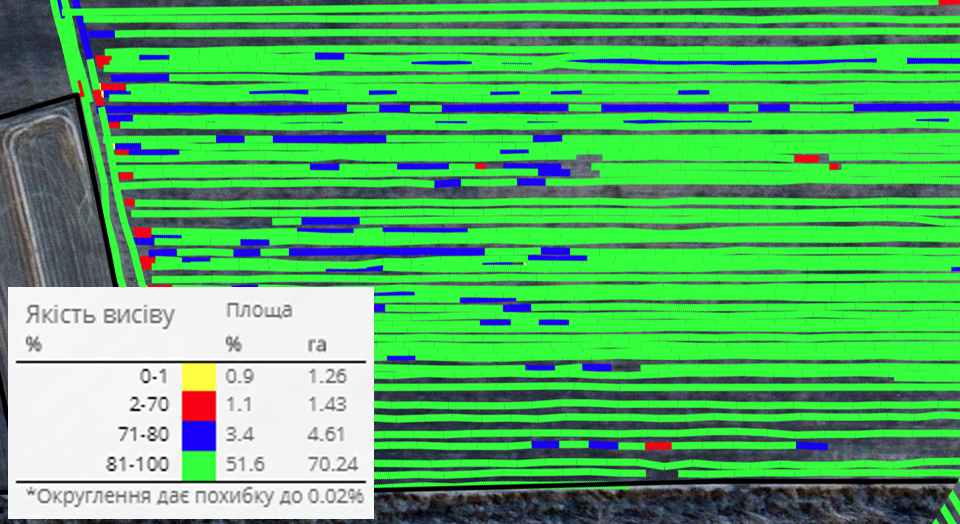
If configured correctly, the online monitoring system indicates deviations arising during sowing (sifting, omissions, double seeds, faulty rows, emergencies) at a time when timely measures can still be taken, and not after the crop has already germinated.
In addition, while work is in the field, the program collects data on all operations performed and builds a detailed seeding map, thanks to which you can not only track the singularity of seeding, but also systematize the necessary information for the next seeding season. Seeding maps make it possible to predict yield, identify problem areas, compare the efficiency of seeders, seed varieties, and optimize fertilizer and seed consumption.
It is possible to prevent downtime and breakdowns of equipment, reduce financial costs and increase profits, but only on condition of timely control and rational use of the information provided.
Back to news list